موقع المشاركة
The electric discharge of the heart
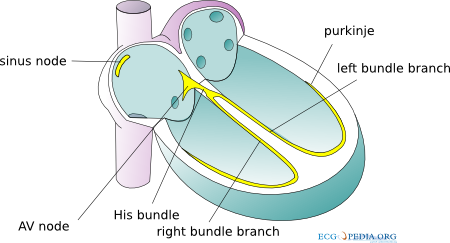
The conduction system of the heart
The sinoatrial node (SA node) contains the fastest physiological pacemaker cells of the heart; therefore, they determine the heart rate.
First the atria depolarize and contract. After that the ventricles
depolarize and contract.
The electrical signal between the atria and the ventricles goes from the
sinus node via the atria to the AV-node (atrioventricular transition)
to the His bundle and subsequently to the right and left bundle
branches, which end in a dense network of Purkinje fibers.
The depolarization of the heart results in an electrical force which has
a direction and magnitude; an electrical vector. This vector changes
every millisecond of the depolarization. In the animation vectors for
atrial depolarization, ventricular depolarization and ventricular
repolarization are shown.
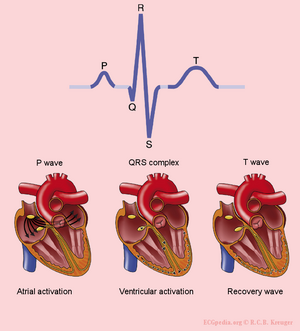
The different ECG waves
The origin of the different waves on the ECG
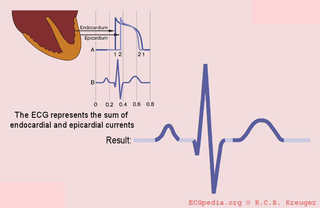
The QRS complex is the average of the depolarization waves of the inner (endocardial) and outer (epicardial) cardiomyocytes. As the endocardial cardiomyocytes depolarize slightly earlier than the outer layers, a typical QRS pattern occurs (figure).
The T wave represents the repolarization of the ventricles. There is no cardiac muscle activity during the T wave.
One heart beat consists of an atrial depolarization --> atrial contraction --> p-wave, ventricular depolarization --> ventricular contraction --> ORS-complex and the resting phase (including the repolarization during the T-wave) between two heart beats.
Have a look at this [animation of the heart cycle]
The origin of the U wave is unknown. This wave possibly results from "afterdepolarizations" of the ventricles.
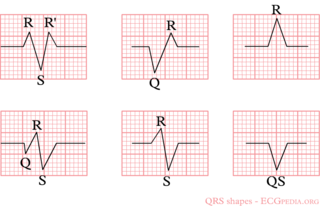
The letters "Q", "R" and "S" are used to describe the QRS complex
- Q: the first negative deflection after the p-wave. If the first deflection is not negative, the Q is absent.
- R: the positive deflection
- S: the negative deflection after the R-wave
- Small print letters (q, r, s) are used to describe deflections of small amplitude. For example: qRS = small q, tall R, deep S.
- R`: is used to describe a second R-wave (as in a right bundle branch block)
The history of the ECG
A concise history of the ECG is presented in a different chapter.The ECG electrodes
Electrical activity going through the heart can be measured by external (skin)electrodes. The electrocardiogram (ECG) registers these activities from electrodes which have been attached onto different places on the body. In total, twelve leads are calculated using ten electrodes.The ten electrodes are:
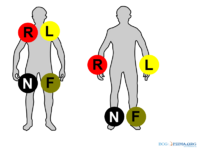
- The four extremity electrodes:
- LA - left arm
- RA - right arm
- N - neutral, on the right leg (= electrical earth, or point zero, to which the electrical current is measured)
- F - foot, on the left leg
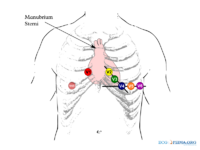
- The six chest electrodes:
- V1 - placed in the 4th intercostal space, right of the sternum
- V2 - placed in the 4th intercostal space, left of the sternum
- V3 - placed between V2 and V4
- V4 - placed 5th intercostal space in the nipple line. Official recommendations are to place V4 under the breast in women.[1]
- V5 - placed between V4 and V6
- V6 - placed in the midaxillary line on the same height as V4 (horizontal line from V4, so not necessarily in the 5th intercostal space)
With the use of these 10 electrodes, 12 leads can be derived. There are 6 extremity leads and 6 precordial leads.
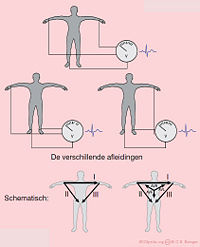
The Extremity Leads
The extremity leads are:- I from the right to the left arm
- II from the right arm to the left leg
- III from the left arm to the left leg
Other extremity leads are:
- AVL points to the left arm
- AVR points to the right arm
- AVF points to the feet
(aVR + aVL + aVF = 0)
The Chest Leads
The precordial, or chest leads, (V1,V2,V3,V4,V5 and V6) 'observe' the depolarization wave in the frontal plane.Example: V1 is close to the right ventricle and the right atrium. Signals in these areas of the heart have the largest signal in this lead. V6 is the closest to the lateral wall of the left ventricle.
ECG variants
Besides the standard 12 lead ECG a couple of variants are in use:- The 3 channel ECG uses 3 or 4 ECG electrodes. Red is on the right, yellow on the left arm, green on the left leg ('sun shines on the grass') and black on the right leg. These basic leads yield enough information for rhythm-monitoring. For determination of ST elevation, these basic leads are inadequate as there is no lead that gives (ST) information about the anterior wall. ST changes registered during 3-4 channel ECG monitoring should prompt acquisition of a 12 lead ECG.
- The 5 channel ECG uses 4 extremitiy leads and 1 precordial lead. This improves ST segment accuracy, but is still inferior to a 12 lead ECG. [2][3]
- In vector electrocardiography the movement of electrical acitivity of the P, QRS and T wave is described. Additional X,Y and Z leads are recorded. Vector electrocardiography is rarely used nowadays, but is sometimes useful in a research setting.
- In body surface mapping several arrays are used to accurately map the cardiac electrical wavefront as it moves over de body surface. With this information the electrical acitivity of the heart can be calculated. This is sometimes used in a research setting.
Color coding of the ECG leads
Two systems for ECG lead color coding are used: the AHA (American Heart Association) system and the IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) system:| AHA (American Heart Association) | IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) | |||
| Location | Inscription | Colour | Inscription | Colour |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right Arm | RA | White | R | Red |
| Left Arm | LA | Black | L | Yellow |
| Right Leg | RL | Green | N | Black |
| Left Leg | LL | Red | F | Green |
| Chest | V1 | Brown/Red | C1 | White/Red |
| Chest | V2 | Brown/Yellow | C2 | White/Yellow |
| Chest | V3 | Brown/Green | C3 | White/Green |
| Chest | V4 | Brown/Blue | C4 | White/Brown |
| Chest | V5 | Brown/Orange | C5 | White/Black |
| Chest | V6 | Brown/Purple | C6 | White/Violet |
Special Leads
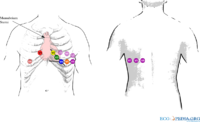
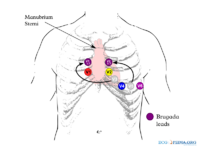
Changed lead positions of leads V3 and V5 to increase the sensitiviy to 'catch' a Brugada pattern on the ECG.
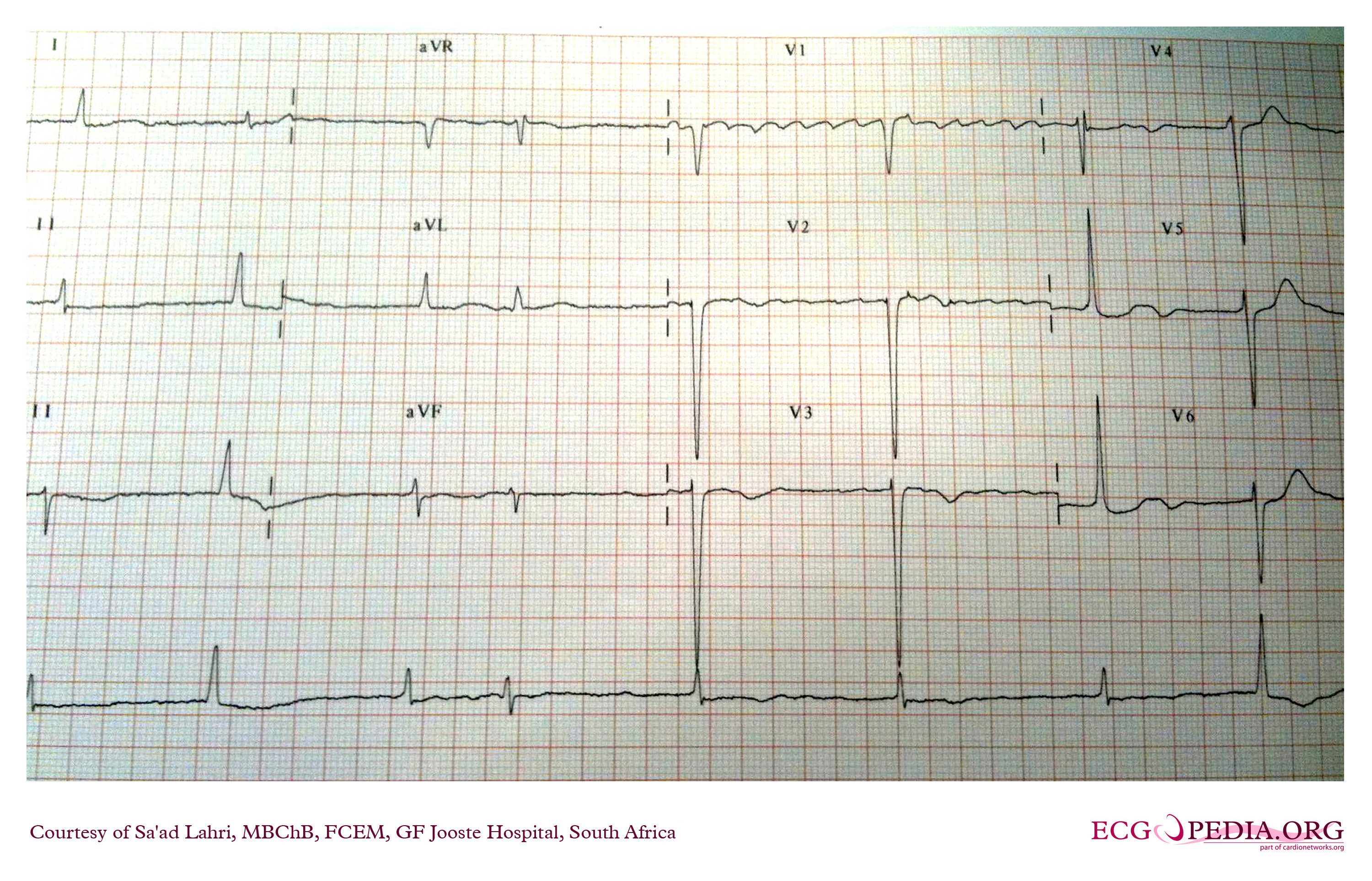
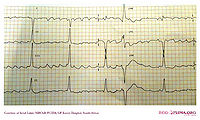
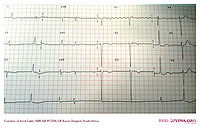
A patient with atrial
fibrillation with a 'Lewis Lead' positioning of the leads. Compared with
the normal lead configuration, the atrial signal is enlarged. Although
some parts have a 'sawtooth' appearance consistent with atrial flutter,
the rhythm is atrial fibrillation as there is a changing pattern in the
atrial activity.
- Leads to improve diagnosis in right ventricular en posterior infarction:
-
-
-
- 1. On a right-sided ECG, V1 and V2 remain on the same place. V3 to V6 are placed on the same place but mirrored on the chest. So V4 is in the middle of the right clavicle. The ECG should be marked as a Right-sided ECG. V4R (V4 but right sided) is a sensitive lead for diagnosing right ventricular infarctions.
-
-
-
-
-
- 2. Leads V7-V8-V9 can be used to diagnose a posterior infarct. After V6, leads are placed towards the back. See the chapter Ischemia for other ways of diagnosing posterior infarction.
-
-
- Leads to improve detection of atrial rhyhtm:
-
- In wide complex tachycardia, good detection of atrial rhythm and atrio-ventricular dissociation can be very helpful in the diagnosis process. An esophagal ECG electrode placed close to the atria can be helpful. Another, less invasive, method is the Lewis Lead. This is recorded by changing the limb electrodes, placing the right arm electrode in the second intercostal space and the left arm electrode in the fourth intercostal space, both to the right of the sternum. Furthermore gain is increased to 20mm/mV and paper speed to 50mm/sec.[4]ß
- Lead positioning to enhance detection of Brugada syndrome
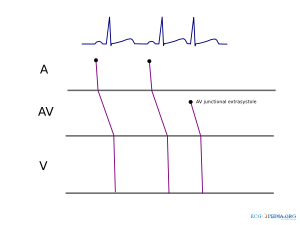
Ladder diagram
A
ladder diagram is a diagram that shows the presumed origin of impulse
formation and conduction in the heart. A = atrial, AV = AV node, V =
ventricles
---------------------------
Technical Problems
Also read the chapter about Technical Problems. That will help you recognize electrical disturbances and lead reversals.References
- Kligfield P, Gettes LS, Bailey JJ, Childers R, Deal BJ, Hancock EW, van Herpen G, Kors JA, Macfarlane P, Mirvis DM, Pahlm O, Rautaharju P, Wagner GS, American Heart Association Electrocardiography and Arrhythmias Committee, Council on Clinical Cardiology., American College of Cardiology Foundation., Heart Rhythm Society., Josephson M, Mason JW, Okin P, Surawicz B, and Wellens H. Recommendations for the standardization and interpretation of the electrocardiogram: part I: The electrocardiogram and its technology: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Electrocardiography and Arrhythmias Committee, Council on Clinical Cardiology; the American College of Cardiology Foundation; and the Heart Rhythm Society: endorsed by the International Society for Computerized Electrocardiology. Circulation. 2007 Mar 13;115(10):1306-24. DOI:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.180200 |
- Rodrigues de Holanda-Miranda W, Furtado FM, Luciano PM, and Pazin-Filho A. Lewis lead enhances atrial activity detection in wide QRS tachycardia. J Emerg Med. 2012 Aug;43(2):e97-9. DOI:10.1016/j.jemermed.2009.08.057 |
- Du Bois-Reymond, E. Untersuchungen über thierische Elektricität. Reimer, Berlin: 1848.
- Hoffa M, Ludwig C. 1850. Einige neue versuche uber herzbewegung. Zeitschrift Rationelle Medizin, 9: 107-144
- Waller AD. A demonstration on man of electromotive changes accompanying the heart's beat. J Physiol (London) 1887;8:229-234
- Einthoven W. Le telecardiogramme. Arch Int de Physiol 1906;4:132-164
- Einthoven W. Über die Form des menschlichen Electrocardiogramms. Pfügers Archiv maart 1895, pagina 101-123
- Marey EJ. Des variations electriques des muscles et du couer en particulier etudies au moyen de l'electrometre de M Lippman. Compres Rendus Hebdomadaires des Seances de l'Acadamie des sciences 1876;82:975-977
- Márquez MF, Colín L, Guevara M, Iturralde P, and Hermosillo AG. Common electrocardiographic artifacts mimicking arrhythmias in ambulatory monitoring. Am Heart J. 2002 Aug;144(2):187-97.
- Hurst JW. Naming of the waves in the ECG, with a brief account of their genesis. Circulation. 1998 Nov 3;98(18):1937-42.
https://drive.google.com/folderview?id=1EZQuRblUO6cQozPH_e4t97PnH40dvcFU
ردحذفhttps://drive.google.com/file/d/11oBS2-Wytdp6u1aq5Z18Aq-415UT_PYS/view?usp=drivesdk
ردحذفhttps://drive.google.com/file/d/1BVi3WrEIOW6ftC-VRiaqAzOmdktuGoJv/view?usp=drivesdk
ردحذفhttps://drive.google.com/file/d/1nxmYBo6wb4I1XuXdbFq1IoMGhlwQuYl_/view?usp=drivesdk
ردحذفhttps://drive.google.com/file/d/1KTnFJ88u53XLk-gzLHq-ljYQMfreeI5x/view?usp=drivesdk
ردحذفhttps://drive.google.com/file/d/1Vis0KYR5cWcKzpqFPWPyZRwTE7IermRT/view?usp=drivesdk
ردحذفhttps://drive.google.com/file/d/1i5Dg5W0viDRlUbXzqN5TrLeWWPpFWevx/view?usp=drivesdk
ردحذف